Chung Lab
Sanghyuk Chung, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Department of Biology and Biochemistry
Office: SERC, 3008
Contact: schung@uh.edu - 832-842-8181
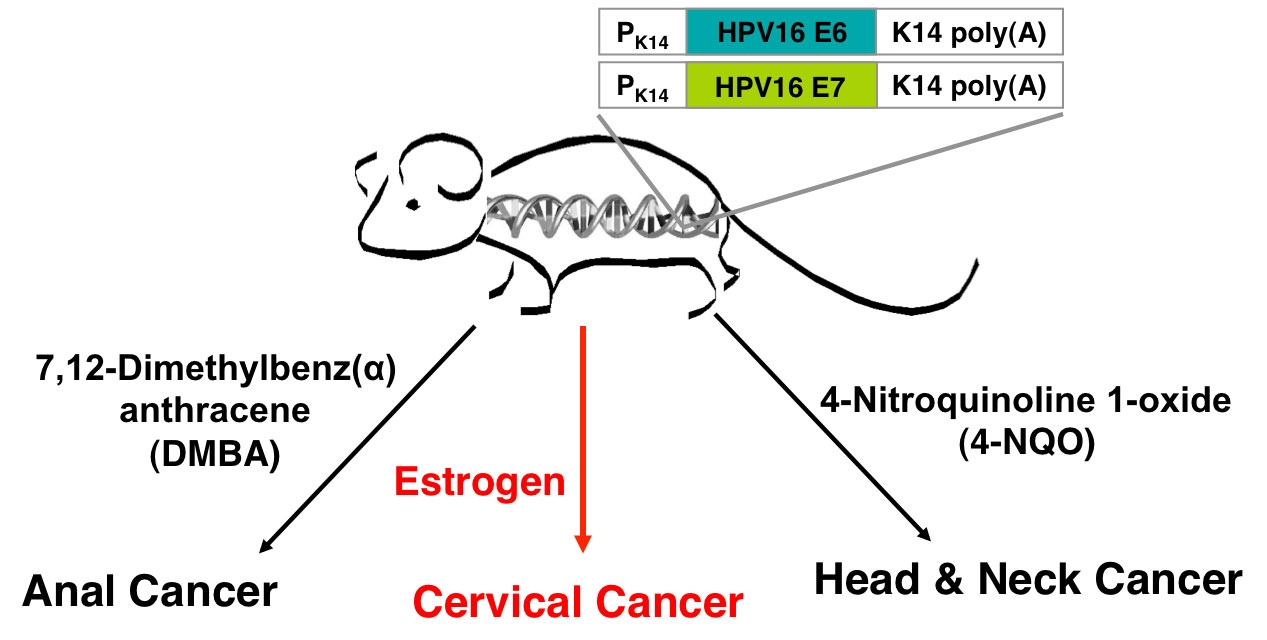
Pathogenesis of HPV-Associated Cancers
Human papillomaviruses (HPVs) cause cancers in various mucosal tissues, including uterine cervix, penis, and head/neck. The tumorigenic potential of HPV mainly stems from viral oncogenes E6 and E7, which inactivate p53 and pRb, respectively. Experimental and epidemiologic evidence indicates that HPV is insufficient for cancer development. Our research focuses on understanding how non-viral factors (e.g., hormones, smoking, and diet) influence HPV-induced cancers. Our studies using the HPV transgenic mice expressing E6 and E7 have demonstrated that stromal estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) is required for the development of cervical cancer. Our results also demonstrated that activation of progesterone receptor (PR) promotes cervical cancer regression. One of our research goals is to understand the molecular mechanism by which ERalpha and PR promote and inhibit cervical cancer, respectively, using various mouse models and cell models. Cigarette smoking is the common cofactor for all HPV-associated cancers. Another research goal is to understand how smoking cooperates with HPV for cancer development and growth, using our novel moues models of vulvar and penile cancer. We anticipate that our studies will not only shed new light on pathogenesis of HPV-associated cancers but also identify therapeutic targets for such cancers.
Recent News
Funding




Sanghyuk Chung, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
Department of Biology and Biochemistry
University of Houston
Houston, Texas 77204-5001
Office: SERC, 3008
Phone: 832-842-8181
schung@uh.edu

MD Saiful Islam Arman
Graduate Student

Ishmael Tetteh
Graduate Student

Sasha Aiurova
Intern

Mohammad Jamali
Undergraduate Intern

Jacque Shavers
Undergraduate Intern
Nabeel Khan
Undergraduate Intern
Behice Neda Yagmur
Undergraduate Intern
- S.A. Lee, C. Ho, M. Troxler, C.Y. Lin, and S.H. Chung. (2021) Non-metabolic Functions of PKM2 Contribute to Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation Induced by the HPV16 E7 Oncoprotein. Viruses. 13:433.
- Y. Park, S. Baik, C. Ho, C.Y. Lin, and S.H. Chung. (2021). Progesterone Receptor Is a Haploinsufficient Tumor Suppressor Gene in Cervical Cancer. Molecular Cancer Research. 19:42-47.
- Baik S, Mehta FF, Chung SH. (2019). Medroxyprogesterone Acetate Prevention of Cervical Cancer through Progesterone Receptor in a Human Papillomavirus Transgenic Mouse Model, Am. J. Pathol. 189: 2459-2468.
- J. Son, Y. Park, and S. H. Chung. (2018). Epithelial Oestrogen Receptor α Is Dispensable for the Development of Oestrogen-Induced Cervical Neoplastic Diseases, J. Pathol. 245:147-152.
- W. Chen, T. Shimane, S. Kawano, A. Alshaikh, S. Kim, S. H. Chung, R. H. Kim, K. Walentin, K. M. Schmidt-Ott, and M. K. Kang. (2018). Human Papillomavirus 16 E6 Induces FoxM1B in Oral Keratinocytes Through GRHL2, J. Dent. Res. 97:795-802.
- Mehta FF, Baik S and Chung SH. 2017. Recurrence of cervical cancer and its resistance to progestin therapy in a mouse model. Oncotarget. 8:2372-2380.
- Mehta FF, Son J, Hewitt SC, Jang E, Lydon JP, Korach KS and Chung SH. 2016. Distinct functions and regulation of epithelial progesterone receptor in the mouse cervix, vagina, and uterus. Oncotarget. 7:17455-17467.
- Chung SH, Targeting female hormone receptors as cervical cancer therapy. (2015) Trends Endocrinol Metab. 26:399-401.
- Spurgeon ME, Chung SH and Lambert PF. 2014. Recurrence of Cervical Cancer in Mice after Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator Therapy. Am. J. Pathol. 184: 530-540.
- Son J, Park JW, Lambert PF and Chung SH. 2014. Requirement of Estrogen Receptor Alpha DNA-Binding Domain for HPV Oncogene-Induced Cervical Carcinogenesis in Mice. Carcinogenesis. 35: 489-496.
- Yoo Y. A., Son, J., Mehta, F. F., DeMayo, F. J., Lydon, J. P., and Chung, S. H. 2013. Progesterone Signaling Inhibits Cervical Carcinogenesis in Mice. Am J Pathol. 183: 1679-1687 (issue highlight)
- Ivanova, M. M., Radde, B. N., Son, J., Mehta, F. F., Chung, S. H., and Klinge, C. M.* 2013. Estradiol and tamoxifen regulate NRF-1 and mitochondrial function in mouse mammary gland and uterus. J Mol Endocrinol. 51: 233-246
- Chung, S. H., Shin, M. K., Korach, K. S., and Lambert, P.F. 2013. Requirement for Stromal Estrogen Receptor Alpha in Cervical Neoplasia. Horm Cancer. 4: 50-59.
- Bonilla-Delgado J., Bulut, G., Liu, X., Cortés-Malagón, E. M., Schlegel, R., Flores-Maldonado, C., Contreras, R. G., Chung, S. H., Lambert, P. F., Uren, A., and Gariglio, P. 2012. The E6 Oncoprotein from HPV16 Enhances the Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin Pathway in Skin Epidermis in vivo. Mol. Cancer Res. 10: 250-258. (Cover)
- Chung SH, Franceschi S, Lambert PF., Estrogen and ERalpha: culprits in cervical cancer? (2010) Trends Endocrinol Metab. 21:504-11.
- Chung, S. H. & Lambert, P. F. 2009. Prevention and Treatment of Cervical Cancer in Mice Using Estrogen Receptor Antagonists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 106: 19467-19472. (In This Issue)
- Chung, S. H., Wiedmeyer, K., Shai, A., Korach, K. S., Lambert, P. F. 2008. Requirement for Estrogen Receptor Alpha in a Mouse Model for Human Papillomavirus-Associated Cervical Cancer. Cancer Res. 68: 9928-9934. (Issue Highlight)
- Chung, S. H., Weiss, R. S., Frese, K. K., Prasad, B. V. V., and Javier, R. T. 2008. Functionally Distinct Monomers and Trimers Produced by a Viral Oncoprotein. Oncogene. 27: 1412-1420.
- Chung, S. H., Frese, K. K., Weiss, R. S., Prasad, B. V. V., and Javier, R. T. 2007. A New Crucial Protein-Interaction Element That Targets the Adenovirus E4-ORF1 Oncoprotein to Membrane Vesicles. J. Virol. 81: 4787-4797.
- Frese, K. K., Latorre, I. J., Chung, S. H., Caruana, G., Bernstein, A., Jones, S. N., Donehower, L. A., Justice, M. J., Garner, C. C., and Javier, R. T. 2006. Oncogenic Function for the Dlg1 Mammalian Homolog of the Drosophila Discs-Large Tumor Suppressor. EMBO J. 25: 1406-1417