UH Researchers Find First New High-Efficiency Thermoelectric Material in 60 Years
Zhifeng Ren led the research group which discovered a new thermoelectric material.University of Houston physicists have discovered a new thermoelectric material offering high performance at temperatures ranging from room temperature up to 300 degrees Celsius, or about 573 degrees Fahrenheit.
“This new material is better than the traditional material, Bismuth telluride, and can be used for waste heat conversion into electricity much more efficiently,” said Zhifeng Ren, M.D. Anderson Chair professor of physics at UH and the lead author of a paper describing the discovery, published online by Nano Energy.
Ren, who is also principal investigator at the Texas Center for Superconductivity at UH, said the work could be important for clean energy research and commercialization at temperatures of about 300 degrees Celsius.
Bismuth telluride has been the standard thermoelectric material since the 1950s and is used primarily for cooling, although it can also be used at temperatures up to 250 C, or 482 F, for power generation, with limited efficiency.
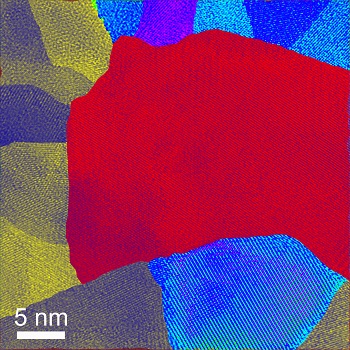
A transmission electron microscope image shows the newly discovered thermoelectric material. The small grains reduce heat conduction, making thermoelectric power generation more efficient.For this discovery, Ren and other members of his lab used a combination of magnesium, silver and antimony to generate electricity from heat using the thermoelectric principle. They added a small amount of nickel, after which Ren said the compound worked even better.
The work was done in collaboration with researchers from the UH Department of Chemistry and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Huaizhou Zhao and Jiehe Sui, a member of Ren’s lab whose home institute is the Harbin Institute of Technology in China, were primary contributors; Zhao is now a research scientist at the Institute of Physics with the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The material works well up to 300 C, Ren said; work to improve its efficiency is ongoing.
The potential for capturing heat – from power plants, industrial smokestacks and even vehicle tailpipes – and converting it into electricity is huge, allowing heat that is currently wasted to be used to generate power. Ren said temperatures there can range from 200 C to 1,000 C, and until now, there hasn’t been a thermoelectric material capable of working once conditions get beyond the lower levels of heat. Much of the demand ranges from 250 C to 300 C, he said.
Ren long has worked in thermoelectrics, among other scientific fields. His research group published an article in the journal Science in 2008 establishing that the efficiency – the technical term is the “figure of merit” – of Bismuth telluride could be increased as much as 20 percent by changing how it is processed. At the time, Ren was at Boston College.
And his lab last summer published a paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences establishing tin telluride with the addition of the chemical element indium as a material capable of converting waste heat to electricity. But tin telluride works best at temperatures higher than about 300 C, or about 573 F, making it important to continue looking for another material that works at lower temperatures.
Ren’s group isn’t the first to study the new material, which has not been named but is referred to in the Nano Energy paper as simply MgAgSb-based materials, using the chemical names for the elements used to create it. The paper cites work done in 2012 by M.J. Kirkham, et al; that work used magnesium, silver and antimony in equal parts, Ren said, but resulted in impurities and poor conducting properties.
He said his lab found that using slightly less silver and antimony, and mixing the elements separately – putting magnesium and silver first in the ball milling process, adding the antimony after several hours – eliminated the impurities and significantly improved the thermoelectric properties.
“We had much different qualities,” he said. “Better, with no impurities, and smaller grain size, along with much better thermoelectric properties.”
- Jeannie Kever, University Communication