- The most important stress opposing a slope's shear stress is imparted by:
running water
earthquakes
frost wedging
gravity
- Water can encourage mass flow by:
reducing friction between grains
undercutting a steep slope
weathering bedrock to clay minerals
all of the above
- A talus cone is produced by a:
rock fall
rock glides
mud flows
all of the above
- Loose, uncemented geologic material is said to be ______.
liquified
crystallized
unconsolidated
consolidated
- Which of the following is the most important factor in causing mass movements?
temperature
pressure
water content
bulk composition
- Which of the following does not promote mass movement?
steep slopes
forest fires
heavy rainfall
all of the above promote mass movement
- The process by which masses of rock and soil move downhill under the influence of gravity is called ______ .
landsliding
mass wasting
hydraulic action
solifluction
- A hill consisting of loose, dry sand that slopes at the angle of repose and has no vegetation _______ .
is stable unless over steepened by excavation
may flow if it becomes saturated with water
will be more stable if vegetation takes root on the hill
all of the above
- One of the most effective ways to stabilize a slope is to:
remove all excess vegetation
increase the rate of compaction - add water
control and remove water
none of the above
- The characteristic slope of a pile of dry sand is called the ______ .
angle of repose
strike
consolidation factor
dip
- Which of the following factors affects the maximum angle at which a slope of loose material is stable?
the amount of moisture
the shape of the particles
the size of the particles
all of the above
- Damp sand has a higher angle of repose than dry sand because of _____ .
cementation
surface tension
partial melting
dissolution
- Surface tension is greatest when ________ .
sand is dry
sand is moist, but not saturated with water
sand is saturated with water
sand is over saturated with water
- Which of the following can trigger a landslide?
an earthquake
a heavy rainstorm
removal of material from the base of a slope
all of these
- During an earthquake, water-saturated sand can behave like a liquid, a process called ____ .
slurrification
solifluction
unconsolidation
liquefaction
- Which of the following statements about mudflows is false?
mudflows tend to move slower than debris flows
mudflows are most common in semi-arid regions
mudflows contain large amounts of water
mudflows can carry large boulders
- Which of the following mass movements is the fastest?
mudflows
debris avalanche
soil creep
earthflow
- What is the dominant force that causes mass movement?
tidal forces
seismic energy release
gravity
wind
- Which of the following processes is not strongly influenced by gravity?
flow of glacial ice
movement of landslides and debris slides
movement of water in streams
all of these are strongly influenced by gravity
- Which of the following statements is false?
round debris forms steeper slopes than angular debris
large debris forms steeper slopes than small debris
dry debris forms steeper slopes than water-saturated debris
moist debris forms steeper slopes than dry debris
- Which of the following situations is least likely to result in mass movement?
a steep slope
a slope with loose material saturated with water
a slope with abundant vegetation
a slope consisting of fractured and deformed rock
- Which of the following has the steepest angle of repose?
fine quartz sand
coarse quartz sand
angular quartz pebbles
all of these have the same angle of repose
- Which of the following situations is most likely to undergo mass wasting?
a dry moderate slope of unconsolidated material
a wet, moderate slope of unconsolidated material
a dry, steep slope of unconsolidated material
a wet, steep slope of unconsolidated material
- As the amount of water in a pile of quartz increases, the angle of repose will _______.
increase
decrease
first increase and then decrease
not change
- Which of the following rock types forms the steepest slopes?
granite
shale
volcanic ash beds
all of these rock types form steep slopes
- Which of the following slopes is least stable?
a slope where the sedimentary layers dip parallel to the slope
a slope where the sedimentary layers are horizontal
a slope where the sedimentary layers dip perpendicular to the slope
all of these slopes have the same stability
- Most of the damage associated with the 1964 Anchorage, Alaska earthquake was caused by _______>
ground shaking during the earthquake
a volcanic eruption triggered by the earthquake
a tsunami (tidal wave) triggered by the earthquake
landslides triggered by the earthquake
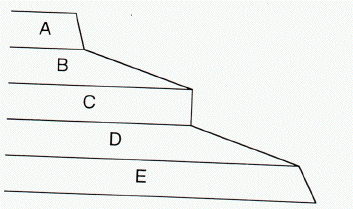
- In the cross section above of the upper part of the Grand Canyon, units B and D are most likely composed of ________.
granite
limestone
sandstone
shale
- Which of the following processes was the major reason why so many landslides occurred during the 1964 Anchorage, Alaska earthquake?
motion along the fault oversteepened slopes
water-saturated sandy layers became liquified by the ground shaking
the earthquake tilted the rock layers downhill
the earthquake caused water to accumulate in the soil
- How do geologists classify mass movements?
by the speed of the mass movement
by the nature of the material
by the nature of the movement
all of these
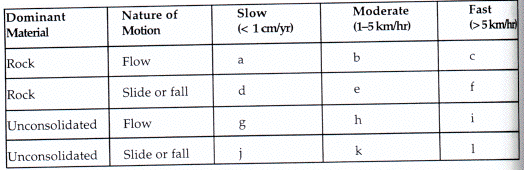
- How would a debris avalanche be classified in this table?
box c
box f
box i
box l
- How would a mudflow be classified in this table?
box a
box b
box g
box h
- How would a slump be classified in this table?
box b
box e
box h
box k
- How would creep be classified in this table?
box a
box e
box g
box k
- How would a rock avalanche be classified in this table?
box b
box c
box e
box f
- The accumulation of rocks at the base of a cliff is called _______.
a dune
soil creep
an alluvial fan
talus
- What is the difference between an earthflow and a debris flow?
Earthflows travel faster than a debris flow
Earthflows travel slower than a debris flow
Earthflows consist of finer material than debris flows
Earthflows consist of coarser material than debris flows
- How fast is soil creep?
a1 to 10 millimeters per year
1 to 10 meters per year
1 kilometer per hour
over 10 kilometers per hour
- Which of the following types of mass movement could a person not outrun?
slump
soil creep
debris flow
debris avalanche
- Why are mudflows and debris avalanches common on volcanic slopes?
because there is abundant unconsolidated volcanic ash
because earthquakes associated with volcanic eruptions can trigger mass movements
volcanic eruptions trigger melting of ice and snow
all of these
- A slow slide of unconsolidated material that travels as a unit is called ______.
slump
soil creep
debris flow
debris avalanche
- Solifluction may occur when ________..
the surface layer freezes while the deeper soil remains unfrozen
the surface soil layer thaws while the deeper soil remains frozen
rapid downhill movement of unconsolidated material moving as unit
rapid downhill movement of unconsolidated material moving like a fluid
- _______ only occurs in permafrost regions.
soil creep
liquefaction
solifluction
landslides
- Why are few mass movement preserved in the geologic record?
mass movements have only occurred recently due to human activities
mass movement deposits erode easily
mass movements were rare in the past due to low rainfall
mas movement deposits are destroyed by large animals
- Mass movements frequently occur at which of the following plate tectonic settings?
convergent
divergent
transform
all of the above